Embark on an extraordinary expedition into the annals of scientific discovery as we traverse the captivating realm of a visionary mind. In this enthralling exploration, we delve into the chronicles of a remarkable individual whose profound insights reshaped our understanding of the natural world. This remarkable individual, armed with an insatiable curiosity, an indomitable spirit, and an unyielding dedication to uncovering the truth, forever altered the course of scientific thought.
Within the pages of this biographical account, we illuminate the path that this exceptional luminary traversed, unraveling the intricate tapestry of his life, his inherent brilliance, and the serendipitous circumstances that propelled his unrivaled contributions. His revolutionary ideas incited ripples of scholarly debate and continue to serve as the foundation upon which the grand edifice of modern evolutionary biology is erected.
Embodied with a profound passion for the natural world, this illustrious figure ventured far beyond the confines of traditional beliefs and ventured into uncharted territories of scientific inquiry. Armed with his meticulous observations, tireless experimentation, and astute analysis, he forever altered the way we perceive not only our own origin but also the flora, fauna, and astounding diversity that populate our planet.
The Early Life of Charles Darwin: From an Inquisitive Child to a Naturalist

In this section, we will delve into the formative years of one of the most celebrated figures in scientific history, Charles Darwin. Beginning with his curious nature as a young boy, we will explore the early experiences and influences that shaped his path towards becoming a renowned naturalist.
During his upbringing, Darwin exhibited a strong sense of wonder and an insatiable curiosity about the world around him. This innate inquisitiveness was evident in his constant exploration of the natural environment, where he developed a keen eye for observing and documenting the intricate details of the flora and fauna he encountered.
- As a young boy, Darwin's passionate interest in collecting various specimens of plants and animals fueled his fascination with the diversity and complexity of life on Earth.
- His encounters with influential figures and mentors further nurtured his burgeoning scientific interests, encouraging him to pursue his intellectual curiosity.
- Notably, his father and grandfather played significant roles in inspiring and supporting his pursuit of knowledge, instilling in him a love for learning and a respect for scientific inquiry.
Through these early experiences and the nurturing of his innate curiosity, Darwin embarked on a journey that would eventually revolutionize the way we understand the natural world. Stay tuned as we explore the transformative events that led Darwin to become the pioneering naturalist he is remembered as today.
Exploring Darwin's Childhood, Education, and Early Scientific Inclinations
In this section, we delve into the early life of the remarkable figure who revolutionized the field of science as we know it today. We shine a light on Charles Darwin's upbringing, his educational journey, and the beginnings of his fascination with the natural world.
A Childhood Shaped by Curiosity: From a tender age, Darwin displayed an insatiable thirst for knowledge and a natural inclination towards exploring the wonders of the natural world. His inquisitive mind, coupled with a keen sense of observation, cultivated the seeds of scientific thought that would later shape his groundbreaking theories.
The Path of Education: Despite initial intentions to follow in his father's footsteps and pursue a career in medicine, Darwin's passion for natural sciences steadily grew. He embarked on a journey of formal education at the University of Edinburgh, where he studied medicine briefly. However, his true passion flourished during his time at Cambridge University, where he cultivated his intellectual faculties under the guidance of influential professors.
An Early Glimpse of Scientific Inclinations: It was during his time at Cambridge that Darwin's scientific interests took root. Engaging with the works of eminent figures such as John Stevens Henslow, a botanist and geologist, and Adam Sedgwick, a renowned geologist, Darwin became immersed in the world of scientific exploration. These formative experiences laid the foundation for his future endeavors and ignited a lifelong commitment to unlocking the mysteries of the natural world.
In the upcoming sections, we will further unravel the fascinating journey of Charles Darwin, tracing his travels, observations, and the development of his groundbreaking theory of evolution through natural selection. Stay tuned to discover the captivating story behind Darwin's exceptional contributions to the scientific community.
The Voyage of the Beagle: Darwin's Transformative Journey
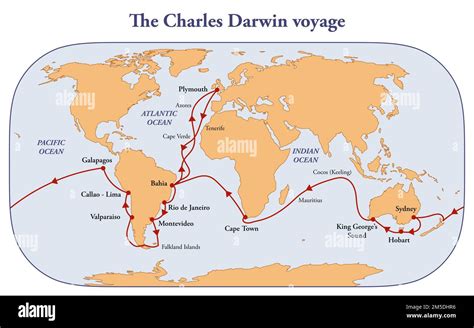
In this section, we delve into Charles Darwin's remarkable expedition aboard the HMS Beagle and explore how it shaped his groundbreaking ideas on evolution and the natural world.
Darwin embarked on a transformative voyage aboard the Beagle, a British naval ship, which took him on a five-year journey around the world. During this expedition, Darwin explored and documented various continents, including South America, Australia, and the Galapagos Islands.
Through his observations, Darwin encountered an astonishing diversity of species and geological formations that challenged the prevailing scientific beliefs of his time. The voyage provided Darwin with extensive firsthand experiences and data, leading him to question the prevailing notion of species' fixity and ultimately laying the foundation for his theory of evolution.
One of the most remarkable stops during the voyage was the Galapagos Islands, where Darwin closely examined the unique wildlife that inhabited the archipelago. He observed variations in finch beak shapes, tortoise shell patterns, and iguana species among the islands, which sparked his curiosity and led to his groundbreaking insights into adaptive radiation and natural selection.
Furthermore, Darwin's time in South America exposed him to the rich biodiversity and geological wonders of the continent. He marveled at the intricate relationships between plants, animals, and their environments, which further fueled his quest to understand the mechanisms behind life's diversity.
To organize and classify his extensive collection of specimens and notes, Darwin implemented a meticulously designed table, allowing him to compare and contrast his findings systematically. This table played a crucial role in crystallizing his thoughts and provided the framework for his future research and the development of his evolutionary theory.
Overall, the voyage of the Beagle acted as a catalyst for Darwin's groundbreaking ideas and revolutionized our understanding of life on Earth. His encounters with diverse ecosystems, unique species, and geological wonders provided him with a wealth of evidence that transformed his worldview and laid the groundwork for his seminal work, "On the Origin of Species".
| Date: | 1831-1836 |
| Location: | South America, Australia, Galapagos Islands, etc. |
| Key Discoveries: | Variations in finch beak shapes, adaptive radiation, natural selection, rich biodiversity of South America |
Unveiling the Crucial Discoveries and Insights from Darwin's Five-Year Expedition
In this section, we delve into the significant findings and profound insights gained throughout Charles Darwin's transformative five-year journey. By embarking on a scientific exploration, Darwin uncovered a wealth of information that would shape our understanding of the natural world.
1. Epiphanies in Species Variation: Darwin observed an astonishing diversity of species during his expedition, from the delicate finches of the Galápagos Islands to the unique ecosystems of the Amazon rainforest. Through meticulous observations and comparisons, Darwin began to perceive the intricate patterns of variation within and between species.
2. The Galápagos Islands and Natural Selection: Darwin's encounter with the diverse Galápagos Islands played a pivotal role in his revolutionary concept of natural selection. Noticing subtle differences in the characteristics of similar species across the islands, he hypothesized that they had diverged from a common ancestor due to their specific environments and selective pressures.
3. Fossils and the Evidence of Evolution: Darwin's expedition took him to various geological formations rich in fossil specimens. These preserved remnants gave him crucial insights into the existence of extinct species and the gradual changes that occurred over time. The fossils provided tangible evidence in support of his theory of evolution.
4. The Diversity of Adaptation: Through his observations, Darwin discovered the extraordinary adaptability of organisms to their environments. He observed how different species possessed unique traits and behaviors that allowed them to thrive in specific ecological niches. This newfound awareness deepened his understanding of the mechanisms behind the survival and reproduction of species.
5. The Role of Geographical Isolation: Darwin recognized the influence of geographical barriers in shaping the distribution and differentiation of species. His observations of isolated populations and the distinct characteristics they developed played a crucial role in the development of his theory of speciation and the concept of common descent.
6. Insights into Human Evolution: While primarily focused on studying other organisms, Darwin's five-year expedition also provided him with valuable insights into the origins and evolution of Homo sapiens. By drawing parallels between humans and other primates, he challenged prevailing beliefs about human exceptionalism and sparked discussions about our place in the natural world.
Through his relentless curiosity and meticulous documentation during his five-year expedition, Charles Darwin laid the foundation for a fundamental shift in our understanding of the natural world and our place within it. His discoveries and insights continue to inspire and guide scientific advancements to this day.
The Theory of Natural Selection: Darwin's Revolutionary Contribution to Science

Discover the groundbreaking concept that shaped the course of scientific understanding and revolutionized biology forever. Charles Darwin's theory of natural selection remains one of the most influential and widely accepted ideas in the field of evolutionary biology. This theory presented a profound shift in our understanding of how species evolve and adapt to their environments.
Darwin's revolutionary theory challenged prevailing beliefs at the time and provided a comprehensive explanation for the diversity of life on Earth. It proposed that species undergo gradual changes over time through a process of natural selection, where individuals with favorable traits have a greater chance of survival and reproduction. This mechanism allows the most adapted individuals to pass on their advantageous traits to future generations, leading to the overall improvement and diversification of species.
By emphasizing the importance of variation within populations, Darwin's theory of natural selection challenged the prevailing belief in fixed and unchanging species. It provided a scientific framework for understanding how species arise, evolve, and adapt, thus laying the foundation for modern evolutionary biology. Natural selection has been validated by numerous scientific studies and observations, confirming its significance as a guiding principle in the field.
Through his meticulous observations, extensive research, and logical reasoning, Darwin's theory of natural selection revolutionized our understanding of the natural world. It showcased the power of science to unravel the mysteries of life and brought forth a new era of inquiry into the mechanisms driving biological diversity. Darwin's innovative ideas continue to shape and influence scientific research, inspiring generations of thinkers and highlighting the importance of evidence-based reasoning in advancing our knowledge of the natural world.
An In-depth Analysis of the Concepts and Evidence behind Darwin's Theory of Evolution
In this section, we will delve into the fundamental concepts and compelling evidence that underpin Charles Darwin's revolutionary theory of evolution, which has shaped our understanding of the natural world. Through a meticulous examination of diverse observations and a meticulous analysis of intricate patterns, Darwin developed a comprehensive framework that elucidates the complexity of life, the unity of species, and the mechanisms driving their gradual transformation over time.
Concepts of Adaptation and Natural Selection: At the core of Darwin's theory lies the concept of adaptation, the remarkable ability of organisms to adjust to their environments through heritable traits. Darwin postulated that the driving force behind adaptation is natural selection, a mechanism that favors the survival and reproduction of individuals with traits better suited to their environments, leading to the propagation of advantageous characteristics over generations. This process gives rise to the astonishing diversity and specialization observed in the natural world.
Evidence from Fossil Records: Darwin's theory finds substantial support in the extensive fossil record, allowing us to observe evolutionary changes over geological time. Fossils provide a snapshot of prehistoric life, allowing scientists to trace the development of specific traits and the emergence of new species. The gradual transition observed in fossil evidence, from simpler to more complex organisms, not only corroborates the theory of evolution but also suggests a continuous process of transformation and speciation.
Biogeographical Patterns: Another compelling line of evidence supporting Darwin's theory is the distribution of species across different geographic regions. Darwin found that species separated by geographically barriers tend to exhibit distinct adaptations suited to their local environments. This observation suggests that the mechanisms of divergence and adaptation occur gradually over time, eventually leading to the formation of distinct species with unique traits in geographically isolated regions.
Analogous Structures: By comparing the anatomical structures of different species, Darwin observed remarkable similarities that served different functions. These analogous structures, such as wings in bats and wings in birds, suggest a common ancestry and point to the process of divergent evolution. Darwin argued that these structures evolved independently in different lineages due to similar selective pressures, providing further evidence for the gradual transformation of species over time.
Molecular Evidence: With advancements in technology, molecular biology has offered compelling evidence for Darwin's theory. By analyzing DNA and proteins, scientists can compare genetic sequences among different species and identify shared genetic material, indicating common ancestry. Molecular evidence has allowed researchers to construct intricate phylogenetic trees, revealing the branching patterns of evolution and providing a molecular confirmation of Darwin's concept of common descent.
Through a meticulous analysis of these concepts and incontrovertible evidence, Charles Darwin's theory of evolution continues to shape our understanding of the natural world, illuminating the intricate mechanisms and ongoing processes that have led to the astounding diversity of life on Earth.
Controversies and Opposition: The Initial Response to Darwin's Ideas

The emergence of Charles Darwin's groundbreaking theories on evolution and natural selection sparked significant controversies and faced widespread opposition during its early stages. The world, at large, grappled with the profound implications these ideas held for traditional beliefs and established ideologies.
Challenging Established Beliefs
Darwin's theories presented a paradigm shift in our understanding of the origins and diversity of life on Earth. They challenged long-held religious and philosophical beliefs that claimed the earth and its species were created by a divine being in a fixed form. The notion of evolution through gradual changes over time was met with skepticism and resistance from religious institutions and adherents of creationism.
Opposing Theories and Scientific Skepticism
The scientific community at the time also met Darwin's ideas with significant skepticism. Many prominent scientists of that era, including established biologists and geologists, held conflicting theories that were incompatible with Darwin's evolutionary concepts. These opposing theories, combined with the lack of substantial empirical evidence initially, resulted in a divided scientific landscape and intense intellectual debates.
Social and Cultural Backlash
Perhaps the most significant opposition Darwin faced came from societal and cultural circles. It was often seen as a direct challenge to the prevailing social hierarchy and the concept of human exceptionalism. Darwin's theories posed a threat to established racial and economic hierarchies, leading to backlash from individuals and groups concerned with maintaining the existing power structures and societal norms.
Public Reaction and Controversial Discussions
The release of Darwin's seminal work, "On the Origin of Species," in 1859 ignited a firestorm of public debate. The book faced backlash from conservative factions who saw it as a direct attack on religious teachings and moral values. Amidst the controversies, scholars, theologians, and scientists engaged in heated discussions, attempting to reconcile or refute Darwin's ideas with their respective disciplines.
Legacy and Ongoing Debates
Despite the initial controversies and opposition, Darwin's ideas gradually gained acceptance over time, eventually becoming the foundation of modern evolutionary biology. However, even to this day, debates surrounding evolution and its implications persist in various spheres, demonstrating the lasting impact and ongoing significance of Darwin's pioneering work.
FAQ
Who was Charles Darwin and what was his contribution to science?
Charles Darwin was a renowned English naturalist and geologist who is best known for his contributions to the theory of evolution. His groundbreaking book "On the Origin of Species" introduced the concept of natural selection, which revolutionized the understanding of how species evolve over time.
What were the key influences on Charles Darwin's work?
Charles Darwin's work was greatly influenced by his observations during his voyage on the HMS Beagle. He traveled to various locations around the world, including the Galapagos Islands, and studied diverse species. Additionally, he was influenced by the ideas of other scientists of his time, such as Thomas Malthus and Jean-Baptiste Lamarck.
How did Charles Darwin's theory of evolution impact the scientific community?
Charles Darwin's theory of evolution had a profound impact on the scientific community. It provided a comprehensive explanation for the diversity of life on Earth and challenged traditional religious beliefs. It sparked extensive debate and further research in the fields of biology, paleontology, and anthropology, and continues to be a critically important and widely accepted scientific theory today.



