Step into the extraordinary world of a revolutionary mind, where boundaries and limitations cease to exist. This is a tale of unparalleled brilliance, a story that captivates and inspires. Join us as we delve into the life and accomplishments of one of history's greatest thinkers.
Unleashing the Power of Curiosity
Imagine a realm where curiosity reigns supreme, where every question spawns a multitude of possibilities. This is the realm that Albert Einstein called home. With an insatiable hunger for knowledge, Einstein challenged the conventions of his time and pushed the boundaries of human understanding.
From Glimpses of the Past to Revolutionary Theories
As we trace the footsteps of this intellectual giant, we uncover the early experiences that shaped his extraordinary mind. From childhood musings to pivotal moments of revelation, each step in Einstein's journey paved the way for his unrivaled contributions to the world of physics.
The Early Life of Albert Einstein: From Modest Beginnings to Scientific Inquisitiveness

In this section, we delve into the formative years of one of the most renowned physicists in history, Albert Einstein. We explore the humble origins from which he emerged and the insatiable thirst for knowledge and curiosity that would shape his remarkable journey.
Birth and Family Background Albert Einstein was born on March 14, 1879, in Ulm, a small city in the Kingdom of Württemberg, Germany. He hailed from a middle-class Jewish family, and his father, Hermann Einstein, was a salesman and engineer, while his mother, Pauline Koch, was a talented pianist. Though not born into affluence, Einstein's upbringing was marked by a strong emphasis on education and intellectual pursuits. |
Early Intellectual Curiosity From an early age, Einstein displayed an insatiable curiosity and exceptional intellectual abilities. He was captivated by mechanical and electrical devices, profoundly inquisitive about the natural world, and had a keen interest in mathematics. These early inclinations laid the foundation for his future scientific endeavors and set him apart from his peers. |
Educational Journey Albert Einstein's educational journey began in Munich, Germany, where he enrolled in a specialized secondary school. His exceptional academic performance and passion for learning opened doors for him, eventually leading to his admission to the Swiss Federal Polytechnic in Zurich. This renowned institution would provide the fertile ground for Einstein's intellectual growth and the exploration of his revolutionary ideas. |
Switzerland and the Patent Office Following his graduation, Einstein faced difficulties in securing a suitable job in academia. He eventually found employment at the Swiss Patent Office in Bern, where he worked as a technical expert. This seemingly mundane occupation not only provided him with a secure income but also granted him ample time to indulge in scientific investigations, ultimately laying the groundwork for his groundbreaking discoveries. |
Albert Einstein's Education: The Foundation for his Future Success
Exploring the educational journey of one of history's greatest minds unveils the building blocks that paved the way for Albert Einstein's remarkable breakthroughs and contributions to science. Understanding the influence of his early education and intellectual development offers valuable insight into the formation of his revolutionary ideas and groundbreaking theories.
From a young age, Einstein's insatiable curiosity and thirst for knowledge set him apart. Despite facing challenges in conventional schooling, his unconventional approach to learning allowed him to develop a unique perspective on the world. The education he received in Switzerland played a crucial role in cultivating his critical thinking skills, fostering his love for mathematics and physics, and nurturing his innate creativity.
| Primary Education | Higher Education |
|---|---|
| Einstein's primary education emphasized the importance of independent thinking and inquiry-based learning. Here, he honed his analytical skills and developed a deep understanding of scientific principles through hands-on experiments and practical applications. | In his quest for further knowledge, Einstein pursued higher education at the renowned Swiss Federal Polytechnic in Zurich. Immersed in an intellectually stimulating environment, he thrived amidst dedicated professors and like-minded peers, engaging in captivating discussions and conducting research that would shape his future. |
| Informal Education | Self-Study and Research |
| Beyond the boundaries of traditional education, Einstein embraced informal learning opportunities. He voraciously read books, delving into a wide range of topics and disciplines, nurturing his intuitive understanding of the world. | Einstein's relentless pursuit of knowledge extended far beyond the confines of the classroom. He devoted countless hours to self-study and conducted groundbreaking research, ultimately challenging existing scientific paradigms and revolutionizing our understanding of the universe. |
Albert Einstein's education acted as the fertile ground on which his genius flourished. Equipped with a solid foundation in scientific principles, a passion for inquiry, and an unwavering determination to unravel the mysteries of the universe, he would go on to reshape the field of physics and leave an indelible mark on scientific history.
Einstein's Earth-Shattering Revelation: The Theory of Relativity and its Profound Impact on Scientific Paradigms
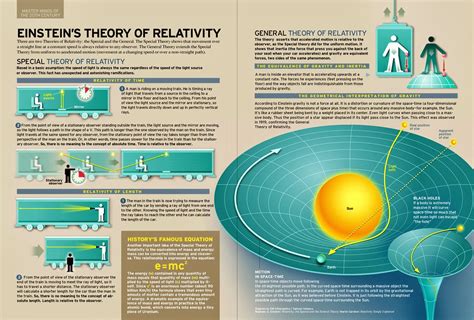
In this section, we delve into one of the most pivotal moments in the annals of scientific history - Einstein's groundbreaking theory of relativity. Without resorting to technical jargon, we'll explore the captivating concepts and far-reaching implications brought forth by this extraordinary scientific achievement.
Like a seismic shift in our understanding of the universe, the theory of relativity revolutionized the way scientists perceive time, space, and gravity. Einstein's genius lay in his ability to challenge the preconceived notions of physics, putting forth a new framework that reconciled seemingly contradictory ideas.
With his theory, Einstein shattered the conventional belief that time flows uniformly regardless of circumstances, propounding instead that time is both relative and flexible. Furthermore, he proposed that the fabric of space and time, known as spacetime, is intrinsically intertwined and can be curved by the presence of massive objects.
Einstein's depiction of gravity as the curvature of spacetime defied classical notions, overthrowing the long-standing Newtonian laws. This revolutionary understanding not only explained previously inexplicable phenomena, such as the bending of starlight in the vicinity of massive celestial bodies but also predicted entirely new phenomena, like the existence of black holes.
The theory of relativity led to a cascade of scientific advancements and breakthroughs. Its profound impact transcended the realm of theoretical physics and extended into various disciplines, including astronomy, cosmology, and even our everyday lives. Technologies such as GPS navigation and nuclear energy owe their existence to our comprehension of the theory.
Einstein's pioneering work remains an enduring testament to the power of human curiosity, ingenuity, and relentless pursuit of knowledge. His theory of relativity continues to spark scientific inquiry and inspire generations of researchers to unravel the mysteries of the universe.
Einstein and the Atomic Bomb: His Contribution to the Manhattan Project
In this section, we will explore Albert Einstein's involvement in the Manhattan Project, a top-secret scientific research program that took place during World War II. Einstein played a significant role in the development of the atomic bomb, although he did not directly participate in its creation or testing. Nevertheless, his groundbreaking scientific theories laid the foundation for the understanding of nuclear energy, which ultimately led to the bomb's realization.
Einstein's theoretical work revolutionized the scientific community and forever changed the world. His groundbreaking equation, E=mc², demonstrated the equivalence of energy and mass, paving the way for the harnessing of atomic energy. Einstein's advocacy for peace and his deep concern over the rise of fascism in Germany prompted him to sign a letter to President Franklin D. Roosevelt, warning about the potential military applications of nuclear chain reactions. The urgency of this letter eventually led to the establishment of the Manhattan Project.
Although Einstein did not directly participate in the development of the atomic bomb, his contribution was invaluable. His scientific theories not only provided the theoretical basis for atomic energy, but also helped shape the thinking of the scientists working on the project. His philosophical beliefs and moral compass also influenced discussions regarding the ethical implications of weaponizing nuclear energy.
- Einstein's correspondence and collaboration with other prominent scientists, such as Leo Szilard and J. Robert Oppenheimer, contributed to the ongoing research and progress of the Manhattan Project.
- Einstein's legacy in the realm of nuclear energy carries both positive and negative connotations. While his theories paved the way for the development of alternative energy sources, they also birthed the destructive power of the atomic bomb.
- The bombings of Hiroshima and Nagasaki in 1945 profoundly affected Einstein. He became a vocal advocate for nuclear disarmament and worked tirelessly to promote peace and prevent the further use of atomic weapons.
Overall, Einstein's involvement in the Manhattan Project showcases the complex interplay between science, politics, and ethics. While his contributions to the understanding of nuclear energy cannot be overstated, his realization of its destructive potential haunted him in the later years of his life. The legacy of Einstein's involvement in the atomic bomb project serves as a reminder of the responsibility scientists bear in considering the broader consequences of their discoveries.
Einstein's Legacy: How His Ideas Continue to Shape Modern Science

The impact of Albert Einstein's intellectual contributions on modern science is nothing short of monumental. His groundbreaking theories and innovative ideas have shaped the way we understand the universe and have paved the way for countless advancements in various scientific fields.
- Einstein's Theory of Relativity: One of the most influential theories in modern physics, Einstein's theory of relativity revolutionized our understanding of space, time, and gravity. His concept of general relativity proposed that gravity is not a force but rather the curvature of space and time caused by mass and energy. This theory completely transformed the field of astrophysics and laid the foundation for numerous discoveries, such as black holes and gravitational waves.
- Photons and Quantum Mechanics: Einstein's pioneering work on the photoelectric effect introduced the concept of photons and their quantized energy, contributing to the development of quantum mechanics. This groundbreaking research not only provided a deeper understanding of the behavior of light but also became an essential cornerstone of modern physics, leading to advancements in fields like quantum computing and cryptography.
- Einstein's Mass-Energy Equivalence: Perhaps the most famous equation in the world, E=mc², stems from Einstein's mass-energy equivalence principle. This equation demonstrates the interconversion and relationship between mass and energy, highlighting the immense potential energy stored within matter. This concept has significantly influenced fields such as nuclear energy and particle physics, contributing to the development of nuclear power and particle accelerators.
- The Unified Field Theory: Einstein dedicated the latter part of his career to the pursuit of a unified field theory–an all-encompassing framework that would unify the forces of nature. Although he was not able to achieve this grand unification, his work laid the groundwork for future physicists to explore and develop theories such as string theory and quantum gravity, seeking to unite the fundamental forces of the universe.
Today, Einstein's ideas continue to shape the forefront of scientific research and inspire scholars worldwide. His intellectual legacy serves as a constant reminder of the power of innovative thinking, persistence, and curiosity–motivating generations to push the boundaries of human knowledge and strive for breakthroughs that will redefine our understanding of the universe.
Einstein's Humanitarian Efforts: The Philosopher behind the Scientist
Delving into the depths of Albert Einstein's legacy, we uncover the profound impact his humanitarian endeavors had on society. Beyond his groundbreaking scientific achievements, Einstein's life was characterized by a dedication to improving the human condition and advocating for social change.
1. Advocacy for Civil Rights: Einstein's unwavering commitment to civil rights sparked from his belief in equality. He actively campaigned against racial segregation and injustice, using his public presence to uplift marginalized communities. Einstein's involvement in civil rights movements set a precedent for future scientific figures to use their influence for social justice.
2. Peace Activism: Einstein's deep desire for global peace led him to become a powerful advocate for disarmament and non-violence. He tirelessly worked towards the prevention of future wars, using his voice and intellect to promote dialogue and diplomacy between nations.
3. Supporting Refugees: Recognizing the plight of those fleeing persecution, Einstein played a pivotal role in assisting refugees during times of crisis. He actively campaigned for improved immigration policies and actively supported organizations working to provide shelter and aid to those in need.
4. Education Advocacy: Einstein firmly believed in the transformative power of education. He championed for accessible and equitable education for all, emphasizing the importance of nurturing intellectual curiosity and critical thinking skills in young minds.
5. Environmental Awareness: Einstein's environmental activism was ahead of its time. His recognition of the impacts of human activities on the planet led him to advocate for sustainable practices and conservation efforts, highlighting the need for responsible stewardship of the Earth's resources.
- Einstein's contributions went beyond scientific theories, embodying the role of a philosopher committed to social betterment.
- By utilizing his platform, Einstein leveraged his influence to fight for justice and equality.
- His humanitarian efforts continue to inspire generations to utilize their own skills and knowledge for the greater good.
In summary, Albert Einstein's profound humanitarian efforts were a testament to his belief in the power of knowledge and his strong conviction to create a better world for all. His contributions as a philosopher and advocate continue to leave an indelible mark on history.
Einstein's Enduring Influence: The Indelible Legacy of a Brilliant Mind

Throughout the annals of history, certain individuals have risen above their peers, leaving an indelible mark on humanity's collective consciousness. One such luminary figure is none other than Albert Einstein. Renowned for his unparalleled intellect and revolutionary insights into the intricacies of the universe, Einstein's name has become synonymous with genius, the embodiment of a mind capable of unraveling the secrets of our existence.
Behind the simplicity of his famous equation E=mc² lies a profound understanding of the fundamental workings of the cosmos. Einstein's groundbreaking theories, from the theory of relativity to his contributions to quantum mechanics, have reshaped our understanding of space, time, and the very fabric of reality itself.
Not only did Einstein challenge prevailing scientific principles, but he also transcended the confines of academia and ventured into the realms of philosophy, ethics, and spirituality. His philosophical musings on the nature of reality, the universe, and the interconnectedness of all things continue to captivate minds and inspire deep contemplation to this day.
Despite his immense intellect, Einstein possessed a unique ability to make complex ideas accessible to the masses. Through his eloquence and relatable approach to science, he was able to bridge the gap between the esoteric realm of theoretical physics and the layperson's understanding. This gift for effective communication helped him garner worldwide recognition and made him an emblematic figure of scientific prowess.
Einstein's influence extends far beyond the field of physics. His ideas have permeated various aspects of society, influencing fields as diverse as art, literature, and even popular culture. His name has become a symbol of intellectual curiosity and the pursuit of knowledge, inspiring countless individuals to question, explore, and push the boundaries of what is possible.
One cannot discuss Einstein's enduring influence without acknowledging his passionate advocacy for social and political causes. Einstein was a staunch supporter of civil rights, pacifism, and the pursuit of world peace. His unwavering commitment to these ideals, coupled with his formidable intellect, lent a powerful voice to various social movements and elevated the discourse surrounding social justice. |
In conclusion, Albert Einstein's legacy is not solely confined to his scientific accomplishments but transcends into a realm of inspiration, enlightenment, and social significance. His unwavering pursuit of truth, his ability to distill complex concepts into comprehensible ideas, and his dedication to fostering a better world have solidified his place in history as a true genius and a guiding light for generations to come.
FAQ
Who was Albert Einstein?
Albert Einstein was a renowned physicist and one of the most influential scientists of the 20th century. He is best known for developing the theory of relativity, which revolutionized our understanding of space, time, and gravity.
What were Albert Einstein's remarkable achievements?
Albert Einstein made several remarkable achievements in his lifetime. His most famous achievement is the theory of relativity, which includes the famous E=mc² equation. He also made significant contributions to the development of quantum theory and explained the photoelectric effect, leading to the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1921.
How did Albert Einstein's theories revolutionize science?
Albert Einstein's theories revolutionized science by challenging traditional notions of space, time, and gravity. His theory of relativity provided a new framework for understanding the universe and introduced concepts like time dilation and the bending of light. This paved the way for advancements in cosmology, astrophysics, and the development of technologies like GPS.
What was Albert Einstein's personal life like?
Albert Einstein had an intriguing personal life. He was a pacifist and a humanitarian, advocating for disarmament and world peace. He had two marriages and had three children. Einstein was also known for his quirky and unconventional personality, with his unkempt appearance and absent-mindedness.
How did Albert Einstein's work impact society beyond the realm of science?
Albert Einstein's work had a profound impact on society beyond the realm of science. His theories and ideas sparked a scientific revolution and influenced the development of modern technology. He became a cultural icon, known for his intellect, creativity, and humanitarian values. His work also inspired generations of scientists and continues to shape our understanding of the universe today.
Who was Albert Einstein?
Albert Einstein was a famous physicist who developed the theory of relativity. He is widely considered one of the most important scientists in history.




