Throughout history, there have been individuals who pushed the boundaries of knowledge, challenging the conventional wisdom of their time and revolutionizing our understanding of the world. In the realm of science, one such visionary was Alfred Wegener, a renowned figure whose contributions continue to shape our understanding of the Earth and its processes. Although his name may not be as widely recognized as some of his contemporaries, the impact of Wegener's work is undeniable, as he unmasked the hidden mysteries of our planet and laid the foundation for modern geological and climatological studies.
Drawing inspiration from his extensive travels and observations, Wegener embarked on a quest to unravel the secrets concealed beneath our feet. With an unwavering spirit and an insatiable thirst for knowledge, he dedicated his life to studying the Earth's phenomenal dynamism, igniting a scientific revolution that would challenge the entrenched beliefs of the time. Stepping beyond the boundaries of established theories, Wegener pioneered a new way of thinking, urging the scientific community to rethink their understanding of the Earth's structure and history.
At the core of Wegener's groundbreaking discoveries was his groundbreaking theory of continental drift–an idea that caused ripples across the scientific community and shook the very foundation of geology. As a fervent advocate, Wegener proposed that the Earth's continents were not static entities fixed in their positions, but were instead in constant motion, drifting across the surface of the planet over vast periods of time. This radical notion, initially met with skepticism and ridicule, challenged the prevailing notion of a stable Earth and forced scientists to reexamine their assumptions.
The Early Life and Education of Alfred Wegener

In this section, we delve into the formative years and academic journey of the esteemed scientist, Alfred Wegener. Exploring his early life and educational background, we gain insights into the factors that shaped his innovative thinking and laid the foundation for his remarkable contributions to the field of geoscience.
From a young age, Wegener displayed a curiosity and passion for the natural world, demonstrating an innate curiosity towards understanding the workings of the Earth. Keenly observing the landscapes and phenomena around him, he developed a profound appreciation for the intricate interconnectedness and dynamic nature of geological processes.
During his educational pursuits, Wegener's insatiable thirst for knowledge led him to immerse himself in a diverse array of disciplines. He pursued studies in physics, astronomy, and meteorology, recognizing their relevance to comprehending the Earth's complex systems. With a fervent desire to integrate scientific disciplines, he honed his skills in mathematics and cartography, enabling him to visually represent and analyze geospatial data effectively.
Wegener's educational journey took him to prestigious institutions renowned for their emphasis on scientific inquiry and exploration. He embraced the opportunity to study under distinguished mentors who instilled in him a sense of intellectual rigor and a commitment to advancing scientific understanding.
Beyond the confines of conventional academic settings, Wegener actively sought practical experience through hands-on fieldwork. Through numerous expeditions, he ventured into remote corners of the globe, meticulously documenting observations of geological phenomena firsthand. These experiences not only strengthened his scientific acumen but also fueled his insatiable curiosity, propelling him towards revolutionary discoveries.
The early life and education of Alfred Wegener were undoubtedly instrumental in nurturing his pioneering spirit and setting him on the path to becoming one of the most influential scientists in history. His interdisciplinary approach and unwavering dedication to unraveling the mysteries of the Earth laid the groundwork for his groundbreaking theory of continental drift, forever altering our understanding of the planet we call home.
Exploring Wegener's formative years and academic journey
In this section, we will delve into the early life and educational path of a visionary scientist who left an indelible mark on the field of geology. We will explore Wegener's upbringing, his early fascination with natural phenomena, and the experiences that shaped his intellectual curiosity.
Starting with his childhood, we will explore the environment and influences that fostered Wegener's curiosity about the natural world. We will examine the pivotal moments and experiences that led him to develop a keen interest in earth sciences, gradually paving the way for his groundbreaking theories and discoveries.
Furthermore, we will trace Wegener's academic journey, highlighting the institutions he attended and the mentors who played a significant role in shaping his scientific perspective. Exploring the subjects he studied and the scientific communities he engaged with, we will gain insight into the multidisciplinary nature of his education and the eclectic range of influences that contributed to his later work.
Additionally, we will discuss the challenges Wegener faced throughout his academic journey, including the prevalent skepticism and resistance he encountered from the scientific establishment. By examining the struggles he faced in gaining recognition for his theories, we will gain a deeper appreciation for the perseverance and determination that characterized Wegener's career.
Lastly, we will reflect upon how Wegener's formative years and academic journey laid the groundwork for his groundbreaking ideas on continental drift. By understanding the cumulative impact of his experiences and education, we can better appreciate the revolutionary nature of his scientific contributions and the enduring legacy he left behind.
Exploring the Genesis of the Continental Drift Hypothesis
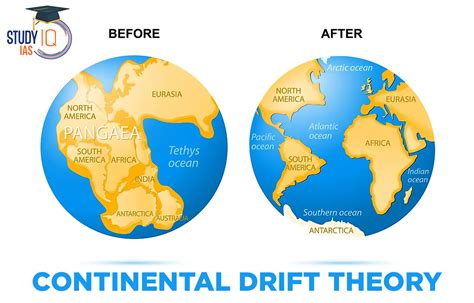
Embarking on a scientific journey challenging prevalent beliefs, one courageous mind catapulted the understanding of Earth's geological history to new heights. This section delves into the remarkable development and evolution of the theory that eventually revolutionized our perception of the Earth's continents – the Continental Drift theory.
The visionary intellect behind this groundbreaking concept sought to unravel the mysteries hidden within the Earth's crust, proposing an audacious hypothesis that would forever alter the field of geology. Carefully examining geological and paleontological data, this pioneering scientist observed striking resemblances between landmasses on different continents, defying conventional wisdom and inspiring a paradigm shift.
- Setting the Foundation: Early Observations and Hypotheses
- Gathering the Pieces: Accumulation of Fossil Evidence
- A Continent in Motion: Pioneering the Concept of Continental Drift
- Skepticism and Opposition: The Struggle for Acceptance
- Modern Validation: Advancements in Technology and Data Analysis
In this exploration of the birth and growth of the Continental Drift theory, we will trace the milestones of scientific discoveries and shed light on the challenges faced by its proponent as they paved the way for a more comprehensive understanding of the Earth's dynamic history.
Exploring Wegener's Revolutionary Hypothesis and Its Reception
Delving into the exceptional theories proposed by Alfred Wegener during his illustrious career, this section highlights the profound impact of his groundbreaking hypothesis on the scientific community. Wegener's visionary idea, often referred to as the continental drift theory, challenged conventional beliefs and sparked a paradigm shift in the understanding of the Earth's geological history.
Wegener's hypothesis postulated that the Earth's continents were once connected as a supercontinent, which he named "Pangaea." He presented compelling evidence, including the fit of the continental coastlines, fossil similarities across distant continents, and geological formations that spanned across present-day continents, indicating their shared history.
This audacious proposal faced significant skepticism and resistance from the scientific establishment initially. Critics questioned Wegener's lack of a plausible mechanism to explain the movement of the continents. They also dismissed his reliance on fossil evidence, which was unconventional at the time. However, over time, further research and discoveries supported Wegener's theory, eventually leading to its widespread acceptance and the birth of the theory of plate tectonics.
Wegener's hypothesis revolutionized the field of geology and geophysics, shattering conventional wisdom and inspiring a fresh perspective on the Earth's geological processes. His visionary ideas continue to impact scientific research and our understanding of our planet's history, underscoring the importance of embracing innovation and challenging established norms in the pursuit of scientific knowledge.
In retrospect, Wegener's perseverance, meticulous research, and audacity to challenge prevailing assumptions highlight his enduring legacy as a pioneer scientist whose contribution reshaped the foundation of modern Earth sciences.
Controversies and Challenges Faced by Wegener

In his pursuit of scientific understanding, Alfred Wegener encountered numerous controversies and challenges that posed significant obstacles to the acceptance of his revolutionary ideas. These obstacles stemmed from the established scientific beliefs of the time, the lack of supporting evidence, and the resistance from the scientific community.
One of the major controversies faced by Wegener was the concept of continental drift. This idea challenged the prevailing belief of fixed continents, with Wegener proposing that the continents were in constant motion driven by geological forces. This drastic departure from the accepted scientific view encountered strong opposition and skepticism.
Additionally, Wegener faced challenges in gathering compelling evidence to support his theory. The lack of a comprehensive geological model and the absence of a clear mechanism to explain how the continents moved hindered the acceptance of his ideas. This led to criticisms and doubts regarding the validity of his proposals.
Moreover, Wegener encountered resistance from the scientific community, with his ideas being met with skepticism and rejection. Many geologists and scientists of the time saw his theory as speculative and lacking a solid foundation. The lack of consensus among experts and the reluctance to challenge long-established ideas further hindered the acceptance of continental drift.
Despite the controversies and challenges, Wegener's perseverance and determination allowed him to make significant contributions to the field of Earth science. His work laid the foundation for the development of the theory of plate tectonics, which revolutionized our understanding of the dynamic nature of Earth's surface and geological processes.
In conclusion, Wegener's journey was marked by controversies, challenges, and opposition. His pioneering ideas faced resistance due to their divergence from traditional beliefs, lack of supporting evidence, and skepticism from the scientific community. However, his contributions and insights ultimately led to a paradigm shift in the field of geology, shaping our understanding of Earth's history and the forces that shape our planet.
Understanding the Resistance and Skepticism Surrounding Continental Drift
The concept of continental drift, which suggests that Earth's continents were once joined together and have since drifted apart, has encountered significant resistance and skepticism throughout its history.
Many scientists and members of the scientific community initially rejected the idea of continental drift due to a lack of concrete evidence and the need for a comprehensive theory to support it. Additionally, the prevailing geologic paradigm at the time, known as static geology, viewed the Earth's crust as unchanging and immobile.
Resistance to continental drift was also fueled by a lack of understanding about the geological processes involved and the mechanisms that could cause the movement of continents. Without a clear understanding of how and why the continents would move, skeptics found it difficult to accept Wegener's theory.
The skepticism surrounding continental drift was further amplified by the limited availability of data and technology during Wegener's time. Without the aid of modern advancements such as satellite imagery and GPS, it was challenging to collect and analyze geological data on a global scale.
The resistance to continental drift was not solely scientific in nature. Cultural and societal factors also played a role in influencing skepticism towards the theory. The idea of continents moving and rearranging over millions of years challenged deeply ingrained notions of stability and permanence.
However, despite the initial resistance and skepticism, Alfred Wegener's perseverance and his presentation of compelling evidence eventually led to the widespread acceptance of the theory of continental drift, revolutionizing our understanding of Earth's geological history.
FAQ
Who was Alfred Wegener and what was his contribution to science?
Alfred Wegener was a pioneering scientist who made significant contributions to the field of geology and meteorology. His most famous contribution was the theory of continental drift, which proposed that the continents were once joined together in a single landmass called Pangaea and have since drifted apart. This theory revolutionized the understanding of Earth's geological history and laid the foundation for the later development of the theory of plate tectonics.
What evidence did Alfred Wegener present to support his theory of continental drift?
Alfred Wegener presented several lines of evidence to support his theory of continental drift. One line of evidence was the fit of the coastlines of different continents, such as Africa and South America. He noticed that the edges of these continents appeared to fit together like puzzle pieces. Wegener also looked at the distribution of fossils and rock formations across different continents, finding similarities that suggested they were once connected. Additionally, he studied the patterns of ancient climates and found evidence of glaciation in regions that are now located closer to the equator, further supporting the idea of continental movement.
Why was Alfred Wegener's theory of continental drift initially met with skepticism?
Initially, Alfred Wegener's theory of continental drift was met with skepticism for several reasons. One reason was the lack of a convincing mechanism to explain how the continents could move. Wegener proposed that the continents plowed through the ocean floor, but this idea seemed implausible at the time. Additionally, Wegener faced opposition from established geologists who held onto the prevailing belief in stationary continents. The scientific community required more evidence and a clearer understanding of the underlying processes before accepting his theory.
How did Alfred Wegener's theory of continental drift eventually gain acceptance?
Alfred Wegener's theory of continental drift eventually gained acceptance as more evidence accumulated over time. One significant development was the discovery of mid-ocean ridges and the mapping of the ocean floor, which provided evidence for tectonic plate movement. Advances in technology, such as satellite observations and paleomagnetic studies, also offered further support for Wegener's ideas. Additionally, the development of the theory of plate tectonics in the 1960s integrated Wegener's ideas with the understanding of Earth's internal processes, ultimately leading to widespread acceptance of his theory.



